Screening
The IONA® test
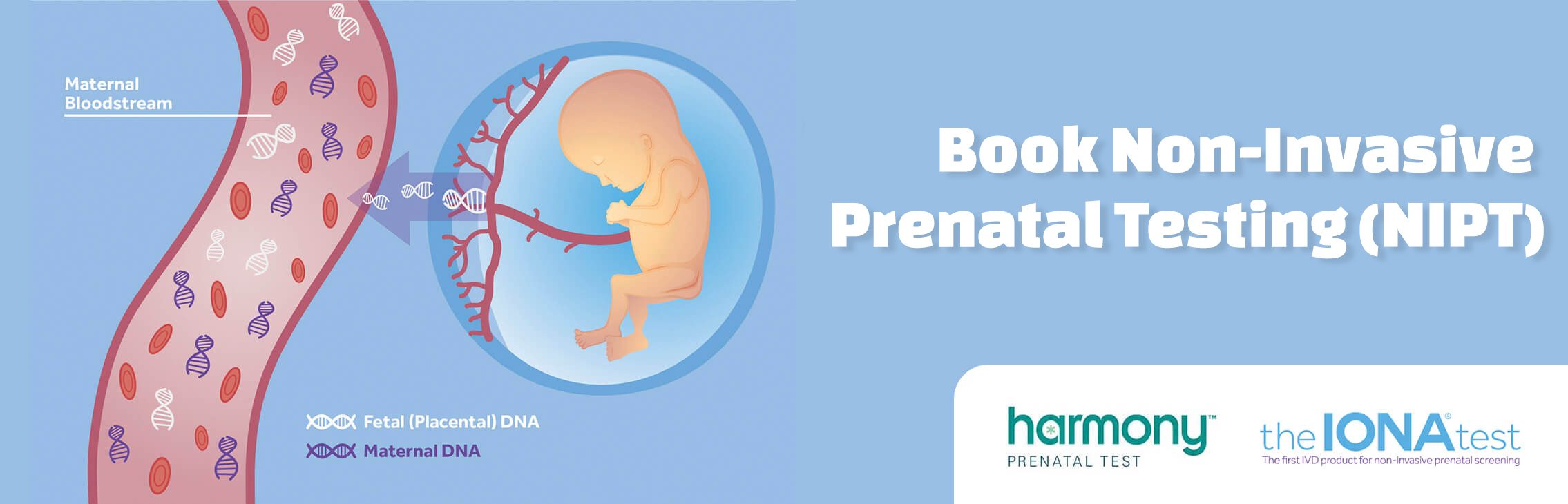
The IONA® test is a non-invasive prenatal test for pregnant women which estimates the risk of a foetus having Down’s syndrome (T21), Edward’s syndrome (T18) and Patau’s Syndrome (T13). The IONA® test can now also test for XY chromosomes to determine the baby’s gender if required.
The IONA® test is an advanced screening test carried out on a small blood sample taken from the mother’s arm with no risk of miscarriage.
Why choose to have the IONA® screening test- NIPT?
Traditional screening that is offered by the NHS during pregnancy is currently called the combined test. This is an ultrasound scan to measure the nuchal translucency (NT) and a blood test. This is much less accurate than NIPT and it only detects around 85% of babies with Down’s syndrome.
The IONA® test has a higher detection rate than the current combined test offered to pregnant women. This means that fewer pregnant women will undergo unnecessary invasive follow-up procedures such as amniocentesis or CVS (chorionic villus sampling) which are stressful, painful and can carry a small risk of miscarriage.
- Safe: non-invasive with no risk of miscarriage
- Fast: results available in 3-5 working days
- Accurate: greater than 99% at detecting trisomy conditions (trisomy 21, 18 and 13) and greater than 97% at detecting fetal sex (optional)
- Local: the IONA® test is performed in a laboratory local to you, not shipped to US or China
- Quality: the IONA® test is a regulated screening test which is CE markedFrom 10 weeks gestation a small blood sample is taken from the mother’s arm and sent to a local laboratory for analysis with the IONA® test. The DNA from the mother’s blood is extracted and the test is performed on the small amount of DNA. During pregnancy, the placenta leaks fetal cell-free DNA which circulates in the maternal bloodstream. As a result, a maternal plasma sample contains a mixture of fetal and maternal circulating DNA. The IONA® test directly measures the amount of cell-free DNA and can detect small changes in the DNA ratio between the maternal and cell-free DNA when a fetal trisomy 21, 18 or 13 is present.
- How are the IONA® results reported?
- The IONA® Software for analysis calculates the relative amount of chromosomes 21, 18 and 13 to calculate a likelihood ratio to predict the presence of a trisomy. This figure is then combined with the mother’s age to calculate the probability of the foetus being affected.
- How the test works
- Low Risk: means that it is very unlikely your pregnancy is affected by trisomy 21, 18 or 13.
- High risk: means that your pregnancy is at increased risk for trisomy 21, 18 or 13 and the result should be confirmed by a follow up invasive such as amniocentesis.
- No result: Very occasionally there is insufficient placental DNA in the sample to obtain a result. Women may be asked back by your healthcare provider for a further blood sample.
For further information please visit www.the-iona-test.com
Price- £439
If you would like to discuss this screening test, or wish to book to have IONA® test carried out please either give us a call or book online
The VeriSeq NIPT Prenatal Test
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) screens for the presence of specific chromosome disorders in the developing fetus. The test analyses fragments of DNA in maternal plasma that have been released from both maternal and placental cells.
NIPT requires a single blood draw, which poses no threat to the fetus, and can be done as early as 10 weeks’ gestation. By analysing the proportions of DNA fragments derived from different chromosomes or chromosome regions, NIPT can screen for the presence or absence of specific chromosome disorders.
NIPT is more accurate than first trimester maternal serum screening and ultrasound in identifying pregnancies with or without these disorders.
 About the test
About the test
DNA from the fetus circulates in the mother’s blood. Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) results from the natural breakdown of fetal cells (presumed to be mostly placental) and clears from the maternal system within hours of giving birth.
During a pregnancy, cfDNA can be tested to give the most accurate screening approach in estimating the risk of a fetus having a common chromosome condition sometimes called a trisomy. This occurs when there are three copies of a particular chromosome instead of the expected two. The test looks to detect the following conditions:
- Trisomy 21 is the most common trisomy at the time of birth. Also called Down syndrome, it is associated with moderate to severe intellectual disabilities and may also lead to digestive disease, congenital heart defects and other malformations.
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) and Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) are associated with a high rate of miscarriage. These babies are born with severe brain abnormalities and often have congenital heart defects as well as other birth defects. Most affected individuals die before or soon after birth, and very few survive beyond the first year of life.
- Sex chromosome conditions occur when there is a missing, extra, or incomplete copy of the X or Y chromosomes. The NIPT test with sex chromosome aneuploidy panel option can assess risk for XXX, XYY, XXY (Klinefelter syndrome), and a missing X chromosome in a girl (Turner syndrome).
In addition, NIPT can assess fetal sex. This is optional (no additional cost).
NIPT does not screen for non-chromosome disorders, familial mutations, malformations, fetal growth or fetal viability.
More details can be seen using the link: Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) | The Doctors Laboratory (tdlpathology.com)
The VeriSeq Prenatal Test determines the risk of fetal trisomies by measuring the relative amount of chromosomes in maternal blood. The VeriSeq test assesses the risks of trisomies 21, 18 and 13 in the fetus, but does not rule out all fetal abnormalities.
Price £469
Please book using Pricelist page

